In today’s technology-rich environment, fostering strong digital citizenship is vital for our students. As educators, we have a significant role to play in equipping them with these essential skills.
The Digital Literacy Framework from British Columbia Ministry of Education, identifies digital citizenship as one of the six key characteristics. While there's a consensus on the importance of cultivating good digital citizens, the overwhelming variety of resources and sometimes conflicting outlines can leave teachers unsure about what to teach and when.
Teacher Librarians in School District 59 have collaborated to collect tools and resources to support teachers, students, and parents from Kindergarten to Grade 9 for developing confident digital citizens. Our goal is to continue to update the collection of lesson plans, websites, and ideas and our digital landscape changes. Your feedback, questions, or contributions are always welcome!
What is Digital Literacy?
Digital Literacy is the interest, attitude and ability of individuals to use digital technology and communication tools appropriately to access, manage, integrate, analyze and evaluate information, construct new knowledge, and create and communicate with others.
- BC Digital Literacy Framework, 2022 British Columbia Ministry of Education. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/education-training/k-12/teach/resources-for-teachers/digital-literacy
Digital citizenship is the ability to navigate our digital environments in a way that's safe and responsible and to actively and respectfully engage in these spaces. - MediaSmarts Canada’s Centre for Digital Media Literacy.
RESOURCES
Teach Digital Citizenship - lessons and activities that help students build essential digital habits and skills. Lessons are grouped in K-2, 3-5, 6-8, 9-12. “Common Sense is the nation's leading nonprofit organization dedicated to improving the lives of all kids and families by providing the trustworthy information, education, and independent voice they need to thrive in the 21st century.”
 https://www.commonsense.org/education
https://www.commonsense.org/education
Reading Media, Media Representation, Ethics & Empathy, Privacy & Security, Community Engagement, Media Health, Consumer Awareness, Finding & Verifying, Making & Remixing. Lessons are grouped in K-3, 4-5, 7-8, 9-12.
“USE, UNDERSTAND & ENGAGE: A Digital Media Literacy Framework for Canadian Schools - Overview
What exactly is digital media literacy, and how can we ensure that students are learning the skills they need in school? MediaSmarts classifies competencies for digital media literacy according to four main principles: access, use, understand and engage. These principles form the basis for our media literacy framework.”
Download the full pdf version here:
https://mediasmarts.ca/sites/default/files/2023-06/digital-media-literacy-framework.pdf
Safer Schools Together
https://saferschoolstogether.com/
Erase
Erase = expect respect & a safe education
“The internet is a great tool. It can also expose us to dangers like cyberbullying, identity theft, online predators or scams. See how you can stay safe online.”
CTRL-F
 https://ctrl-f.ca/en/
https://ctrl-f.ca/en/
Named for the keyboard shortcut for ‘find,’ the CTRL-F digital media literacy program equips students with the habits and skills they need to find and evaluate online information, and to determine what to trust.
The CTRL-F Online Search Skills lessons teach students how to effectively use search engines and assess search results to find relevant and reliable information.
Lessons feature games, videos, and activities that are ideal for students in grades 4 to 8, or for anyone who needs a refresher on some of the fundamentals.
The CTRL-F Verification Skills lessons help students learn to evaluate online sources and claims to determine what to trust, using the evidence-based ‘lateral reading’ strategies.
Lessons feature expert-led videos, live web examples and walkthroughs and were designed for students in grades 7 to 12.
BC Ministry of Education
“Digital literacy is an important skill to have in today's technology based world.
The Ministry of Education and Child Care defines digital literacy as “the interest, attitude and ability of individuals to appropriately use digital technology and communication tools to access, manage, integrate, analyze and evaluate information, construct new knowledge, create and communicate with others”.
The Digital Literacy Framework (PDF) elaborates on six characteristics identified by B.C. educational leaders. These characteristics are based on the National Educational Technology Standards for Students (NETS•S) standards developed by the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) and encompass the types of knowledge and skills learners need to be successful in the 21st century.”
“Digital literacy and the use of AI in education: supports for British Columbia schools”
“Considerations for Using AI Tools in K-12 Schools” pdf
Digital Citizenship in the Classroom - Bringing Digital Citizenship to the classroom in meaningful ways.

District Resource Centre
Digital Citizenship Resources at the DRC
LESSON SUPPORTS
Grades 6-12
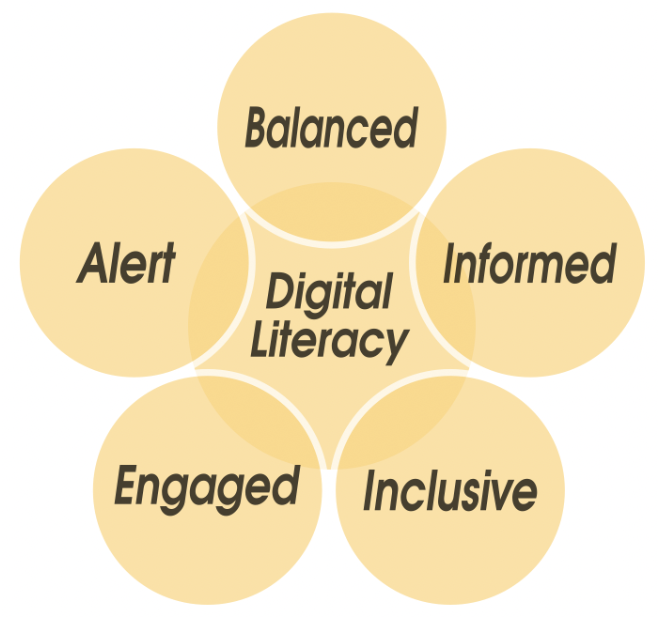
Balanced
Students participate in a healthy variety of online activities and know how to prioritize their time between virtual and physical activities.
Is aware of his/her media habits and the array of media he/she uses on a weekly basis, and the role of digital media in his/her life (Gr. 6-9).
Exhibits a positive attitude toward using technology that supports collaboration, learning, and productivity (Gr. 6-9).
Has a positive, but realistic attitude towards the benefits and risks associated with information technologies (Gr. 6-9).
Exhibits leadership as a digital citizen (Gr. 10-12).
Is aware of the discourse on both the issues and the opportunities involved in new media (Gr. 10-12).
Arranges and develop his/her personal working environment as an effective and reliable system (Gr. 6-9).
Uses different ICT in a way that helps to achieve certain results more quickly, or more easily, or to achieve better results (Gr. 6-9).
Informed
Students evaluate the accuracy, perspective and validity of digital media, and have developed critical skills for curating information from digital sources. (needs a statement about social media and the problem. A digitally literate person understands the nature of self-image and identity in the online environment, how our perceptions of others and our social values may be manipulated, and that people may not be what or whom they appear to be online.
Stays informed using a combination of active search and personalised, automated delivery of information (Gr. 10-12).
Understands the social nature of digital media and technologies, and has basic vocabulary and knowledge for discussing the media landscape (Gr. 6-9) .
Understands that anyone can publish on the Web, so not all sites are equally trustworthy.
Understands that to conduct effective and efficient online searches, he/she must use a
variety of searching strategies.
Locates, organizes, analyzes, synthesizes, and ethically uses information.
Understands both the benefits and drawbacks of using collective intelligence, (crowdsourcing), in different contexts.
Evaluates and selects information sources and digital tools based on the appropriateness to specific tasks.
Compares, contrasts, and synthesizes information from diverse sources (triangulates information) before it is used in a knowledge-making process.
Gathers relevant digital information, e.g. other users’ experiences, and assesses the quality of goods based on that information.
Integrates, compares and puts together different types of information related to multimodal content
Structures, classifies, and organizes digital information/content according to a certain classification schemes or genres.
How to search the internet effectively
Understands the role of ICT (Information and Computer Technology) in everyday life, in social life and at work. (Gr. 6-9)
Is aware of environmental issues related to the use of digital technologies. (Gr. 6-9)
Is aware of the general trends within new media even if he/she does not use them. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands the wider context of digital tools in a 'digital age' characterised by globalisation and networks. (Gr. 10-12)
Selects and uses applications effectively and productively (e.g. chooses the most appropriate technologies according to the task). (Gr. 6-9)
Understands the potential of digital devices and resources for her/his schoolwork. (Gr. 6-9)
Knows the range of things that can be done using ICT/Internet. (Gr. 6-9)
Is aware of the most relevant or popular digital technologies used by others (e.g. peers, professionals). (Gr. 10-12)
Has reasonable knowledge of available technologies, their strengths and weaknesses and is able to make informed decisions about whether and how to use technologies to pursue personal goals. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands the technologies he/she is using at a level that is sufficient to underpin good purchasing decisions (e.g. devices or Internet Service Providers). (Gr. 10-12)
Uses ICT resources to safely expand his/her own knowledge and connect to the world. (Gr. 6-9)
Learns how to work with any new digital technology by trying it out, and using its internal guidance and help. (Gr. 6-9)
Adapts smoothly to new technology, and learns how to use them, and integrates them into his/her environment. (Gr. 6-9)
Self-monitors personal goals and diagnoses deficiencies of digital competence required for reaching these goals. (Gr. 6-9)
Uses learning management systems, information management systems, etc. (Gr. 10-12)
Exploits technological potentials in order to represent and solve problems. (Gr. 10-12)
Solves technical problems and knows what to do when technology does not function. (Gr. 10-12)
Transfers current knowledge to learning new technologies. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands the concepts of ethical behaviour and online ethics. (Gr. 10-12)
Inclusive Critical Thinkers
Students are critical thinkers and open to hearing and recognizing multiple viewpoints, and engaging with others online with respect and empathy.
Uses digital technology to identify and define authentic problems and significant questions for investigation.
Uses digital technology to plan and manage activities to develop a solution or complete a project.
Creates knowledge representations (e.g. mind maps, diagrams) using digital media.
Creates complex models and simulations of the real world using digital information.
Considers both the benefits and drawbacks of using collective intelligence (crowdsourcing) in different contexts.
Interacts, collaborates, co-constructs content, and publishes with peers, experts, or others employing a variety of digital environments and media. (Gr. 6-9)
Communicates information and ideas effectively to multiple audiences using a variety of media and formats. (Gr. 6-9)
Contributes to project teams to produce original works or solve problems. (Gr. 6-9)
Communicates through ICT (e.g. email, instant messaging, video conferencing). (Gr. 6-9)
Solves a theoretical or practical problems, of individual or collective interest, through or with the support of digital tools (Gr. 10-12).
Engaged
Students use technology and digital channels to solve problems and be a force for good in their families and communities. (Students are aware of the benefits and risks of social media and is aware of their digital foot print. Add ethics Reword)( Is aware of how he/she and others represent themselves online, and the relationship between online and offline selves.) A digitally literate person is aware that his/her activities on the Internet leave a permanent "digital footprint" or "trail" and behaves accordingly. A digitally literate person recognizes cyberbullying and knows how to deal with it.
Can identify and participate responsibly in online networks that foster positive community.
Searches, collects, process, evaluates, shares, and stores data and information using various devices, applications, or cloud services. (Gr. 6-9)
Participates in society through online engagement in democratic actions (e.g. lobbying, petitions, parliament). (Gr. 6-9)
Knows how to use social media and social networks to promote results of their work. (Gr. 10-12)
Conducts transactions online (e.g. pay bills, apply for a job, submit tax declaration, complete online forms, book a hotel, interact with government or local services, shop online, etc.). (Gr. 10-12)
Understands how meaning is produced through multimedia (text, images, audio, video) and how culture is produced through the Internet and social media in particular.
Consults digital resources as a matter of routine across various aspects of life (news, health, sports, travel, entertainment, etc.). (Gr. 10-12)
Uses social media and participative technology. (Gr. 10-12)
Uses digital media to be part of a community. (Gr. 10-12)
Has an advanced sense of suitable behaviour, finely tuned to media context, audience and legal provisions.
Makes valuable contributions to the public knowledge domain (e.g. wikis, public forums, reviews). (Gr. 10-12)
Exhibits leadership as a digital citizen
Makes valuable contributions to the public knowledge domain (e.g. wikis, public forums, reviews).
Can identify and participate responsibly in online networks that foster positive community. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands the concepts of ethical behaviour and online ethics. (Gr. 10-12)
Alert
Students are aware of their digital actions and know how to be safe and create safe spaces for others online (another statement about cyber bullying)
RCMP Lesson Plan for 6-8 (I have the PDF)
Digital Foot Print and Identity
Book: Behind Their Screens: What Teens Are Facing (And Adults Are Missing)
Harvard: Teens in a Digital World
Everything you need to teach Digital Citicenship
Is aware of the gender stereotypes that exist in video games, virtual worlds and elsewhere on the Internet (Gr. 6-9).
Understands the different pressures teens face when it comes to editing, posting, and commenting on photos online (Gr. 10-12).
Is aware of how he/she and others represent themselves online, and the relationship between online and offline selves (Gr. 10-12).
Is aware that he/she has a digital footprint and that this information can be searched, copied, and passed on, and that he/she can take some control based on what he/she posts online. (6-9)
Understands the benefits of sharing information online and the potential risks of sharing inappropriate information. (Gr. 9-12).
Understands his/her responsibility to protect the privacy of others when posting information about them online. (Gr. 9-12)
Understands that everything they or anyone else posts about them online becomes part of a public online presence known as a digital footprint. (Gr. 9-12)
Acknowledges the benefits of online talk and messaging, but knows how to handle situations or online behavior which may make them feel uncomfortable. (Gr. 6-9)
Advocates and practices safe, legal, and responsible use of information and technology (Gr. 10-12).
Understands that presenting themselves in different ways online carries both benefits and risks (Gr. 6-9).
Understands the concept of privacy in their everyday lives, and as it relates to using the Internet.
Understands the ways websites and companies collect data online and utilize it to personalize content for their users, as well as consider companies’ motives in doing so.
Understands the security implications of computer networks and client/server
Assesses and reduces/avoids technology related threats to his/her health (Gr. 6-9).
Has a general level of confidence to experiment with new technologies, but also to reject inappropriate technologies (Gr. 6-9).
Manages the potentially distracting aspects of working digitally. (Gr. 6-9) exhibits a positive attitude towards learning about emerging digital technologies (Gr.6-9).
Appreciates that cruelty can escalate quickly online because people are often anonymous and posts spread quickly
Understands the dynamics of online cruelty and how it affects all of the people involved.
Understands the benefits of sharing information online and the potential risks of sharing inappropriate information.
Understands that everything they or anyone else posts about them online becomes part of a public online presence known as a digital footprint.
Understands his/her responsibility to protect the privacy of others when posting information about them online.
Understands the different pressures teens face when it comes to editing, posting, and commenting on photos online.
Advocates and practices safe, legal, and responsible use of information and technology.
Is aware of the discourse on both the issues and the opportunities involved in new media.
Understands the wider context of digital tools in a 'digital age' characterised by globalisation and networks.
Distinguishes good-natured teasing from cyberbullying. (Gr. 6-9)
Understands the difference between being a passive bystander and an active intervener in cyberbullying situations. (Gr. 6-9)
Appreciates that cruelty can escalate quickly online because people are often anonymous and posts spread quickly. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands the dynamics of online cruelty and how it affects all of the people involved. (Gr. 10-12)
Thinks critically about the risks and responsibilities of developing relationships with people online. (Gr. 10-12)
Creative and Inovative
Remixes different existing digital content into something new
Understands the different purposes and contexts of digital image editing.
Is aware of the general trends within new media even if he/she does not use them.
Understands the wider context of digital tools in a 'digital age' characterised by globalisation and networks.
Knows how to use social media and social networks to promote results of their work.
Uses a variety of programming languages to create programs, apps, games, or other software tools.
Is familiar with the meaning of terms commonly used in user manuals for the operation of hardware and the installation and configuration of software
Considers both the benefits and drawbacks of using collective intelligence (crowdsourcing) in different contexts. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands copyright and licence rules, fair use, and the rights he/she has as a creator. (Gr. 6-9)
Understands the legal and ethical dimensions of respecting creative work. (Gr. 10-12)
Distinguishes between taking inspiration from the creative work of others and
appropriating that work without permission. (Gr. 10-12)
Understands the legal and ethical dimensions of respecting creative work
Distinguishes between taking inspiration from the creative work of others and appropriating that work without permission.
Knows there are different ways of licensing intellectual property production, understands differences between using copyright, public domain, “Copyleft” and/or creative commons licenses.
Technology Operations and Concepts
Troubleshoots systems and applications.
Conducts transactions online (e.g. pay bills, apply for a job, submit tax declaration, complete online forms, book a hotel, interact with government or local services, shop online, etc.).
Consults digital resources as a matter of routine across various aspects of life (news, health, sports, travel, entertainment, etc.).
Is aware of the most relevant or popular digital technologies used by others (e.g. peers, professionals).
Has reasonable knowledge of available technologies, their strengths and weaknesses, and is able to make informed decisions about whether and how to use technologies to pursue personal goals
Understands the technologies he/she is using at a level that is sufficient to underpin good purchasing decisions (e.g. devices or Internet Service Providers).
Solves a theoretical or practical problems, of individual or collective interest, through or with the support of digital tools
Stays informed using a combination of active search and personalised, automated delivery of information
uses learning management systems, information management systems, etc.
exploits technological potentials in order to represent and solve problems.
solves technical problems and knows what to do when technology does not function.
transfers current knowledge to learning new technologies.



